
What are AI Agents
AI agents are software programs that use artificial intelligence to perform tasks on their own. It learns from data, adapts to new information, and makes decisions or provides help. Examples include virtual assistants, chatbots, and recommendation systems.
Imagine having numerous tasks to complete and a team of employees to handle them. Now, picture intelligent programs—AI Agents—that can perform these tasks even more efficiently. These AI Agents make decisions, manage interactions, and streamline processes with remarkable precision and speed, turning routine tasks into exceptional outcomes.
How do AI Agents work?
AI Agents perceive their environment and take actions using a mix of rule-based systems, decision-makers, and machine learning. They process past and present data to pursue optimal outcomes, continually adapting and evolving to achieve their goals.
Autonomous Problem Solvers
Unlike traditional AI, which needs specific prompts, AI Agents operate on their own. They are driven by goals, taking on tasks without constant input. This independence lets them adapt to new information and environments smoothly.
Beyond Standard Automation
AI Agents shine in uncertain situations, managing vast data streams and exploring new areas. They represent the next level of intelligent automation, performing tasks like browsing the internet, managing apps, conducting financial transactions, and controlling devices.
A Step Towards AGI
The rise of AI Agents is a significant step toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). These agents show human-like flexibility, mastering various tasks and indicating a major shift toward an unprecedented future.
Interactive and Adaptive
AI Agents continuously learn and adjust, trying out new solutions to achieve their goals. Their ability to spot and fix mistakes makes them perfect for complex and unpredictable tasks.
Types of AI Agents
1. Simple Reflex Agent
A simple reflex agent operates by following a set of predefined rules to make decisions. It reacts solely to the current situation, without taking into account past events or future consequences.
This type of agent is ideal for environments with stable rules and straightforward actions, as its behavior is purely reactive and responsive to immediate changes in the environment.
Example:
A vending machine serves as an example of a simple reflex agent. It operates based on a straightforward condition-action rule, when a coin is inserted, and a selection is made, it dispenses the corresponding product. This process does not involve any memory or consideration of past actions, it simply reacts to the current input, demonstrating the fundamental principle of a simple reflex agent.
2. Model-based Reflex Agent
A model-based reflex agent takes actions based on its current perception and an internal state that represents the unobservable aspects of the world. It updates its internal state by considering:
How the world changes independently of the agent How the agent’s actions influence the world
Example:
Amazon Bedrock is a premier example of a cautionary model-based reflex agent, utilizing foundational models to simulate operations, gain insights, and make informed decisions for effective planning and optimization. By continuously refining its models with real-world data, Bedrock adapts and optimizes operations, predicts outcomes, and selects optimal strategies through scenario planning and parameter adjustments.
3. Goal-based Agents
Goal-based agents are designed to use information from their environment to achieve specific objectives. They use search algorithms to identify the most efficient path to reach their goals within a given environment.
Also known as rule-based agents, these systems follow pre-established rules to achieve their objectives, taking specific actions based on certain conditions. They are relatively easy to design and can manage complex tasks, making them suitable for applications in robotics, computer vision, and natural language processing.
Example:
We can say that ChatGPT is a goal-based agent and also a learning agent. As a goal-based agent, it aims to provide high-quality responses to user queries. It chooses actions that are likely to assist users in finding the information they seek and achieving their desired goal of obtaining accurate and helpful responses.
4. Utility-based Agents
Utility-based agents make decisions aimed at maximizing a utility function or value. They select actions that offer the highest expected utility, which measures the desirability of an outcome.
These agents are well-suited for handling complex and uncertain situations with flexibility and adaptability. They are commonly used in scenarios where they need to compare and choose between multiple options, such as in resource allocation, scheduling, and game-playing.
Example:
One example of a utility-based AI agent is the route recommendation system used by Google Maps. This system solves the problem of finding the 'best' route to reach a destination. Google Maps evaluates multiple factors, such as current traffic conditions, distance, and estimated travel time, to determine the most efficient route for the user. By continuously updating and optimizing these variables, Google Maps helps users achieve their goal of reaching their destination in the quickest and most convenient way possible.
5. Hierarchical Agent
A Hierarchical Agent is an advanced AI tool that helps businesses manage and optimize complex operations across different levels. It efficiently allocates tasks and responsibilities based on the skill levels and expertise of team members. This system allows businesses to monitor team performance, improve communication, and increase productivity.
Structured in a hierarchical model, these agents consist of various levels or modules. Each level handles a specific subtask and communicates with both higher and lower levels to exchange information and work towards the overall goal. Lower-level agents focus on detailed, specific tasks, while higher-level agents coordinate and manage these tasks. This structure distributes the workload, improves efficiency, and solves complex problems by breaking them into simpler parts, enhancing overall performance through effective information sharing and decision-making.
6. Learning agents
Learning agents are AI systems that improve their performance over time by learning from data and experiences. They use machine learning techniques to adapt and make better decisions as they gather more information.
These agents acquire knowledge and enhance their performance through different learning methods like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. In supervised learning, agents are trained with labeled data to recognize patterns and make predictions. Unsupervised learning allows agents to explore data independently, uncovering hidden patterns without prior knowledge. Reinforcement learning involves agents interacting with their environment, learning optimal strategies through rewards and penalties based on their actions.
Examples of AI Agents:
AI Fashion Assistant
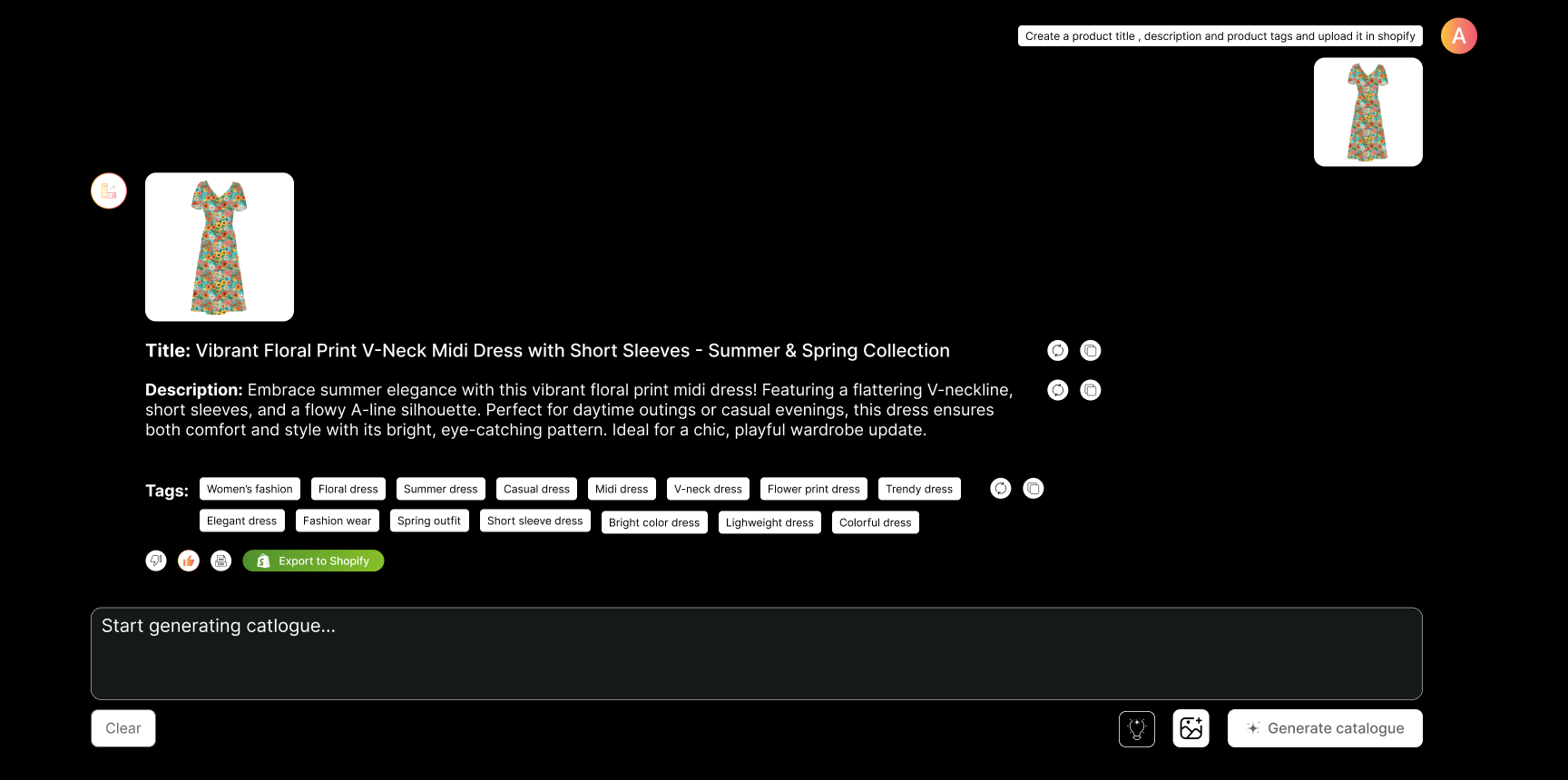
User Uploads a Dress Image: The user uploads an image of a dress they are interested in.
Provide Dress Details: The user is asked to provide details about the dress, such as:
a. Cloth Type (e.g., cotton, silk)
b. Size (e.g., S, M, L)
c. Occasion (e.g., party, office, casual)
Model Training: The AI uses these details to train its model, learning to recognize similar attributes in other dresses.
Analyze New Dresses: The user can upload more dress images, and the AI will identify the cloth type, size, and occasion based on the trained model.
Confirm and Adjust: The user can confirm or correct the AI's suggestions, further refining the model.
AI Agents for Computer Vision
AI agents for computer vision are transforming how we process and analyze visual data. These agents can compile vast amounts of images and videos, train models, and deploy them in real-time applications. For instance, they can identify objects in security footage, assist in medical image analysis, and even enable autonomous vehicles to navigate safely. Their ability to understand and interpret visual information makes them invaluable across various industries, providing real-time insights and enhancing operational efficiency.
Autonomous Robots
When it comes to handling physical tasks, our robotic helpers are real game-changers. These independent machines excel in various settings, doing everything from household chores to industrial heavy lifting. Consider those smart vacuum cleaners that roam around our homes, keeping them clean without any fuss. Or take a peek into Amazon’s warehouses, where robots efficiently sort and transport items, streamlining the whole operation. These robots are more than just machines; they’re equipped with advanced sensors and AI smarts that allow them to understand their surroundings, make intelligent choices, and carry out tasks with barely any human help needed.
AI Agents for Personal Assistants
AI-powered personal assistants have become increasingly common in our daily lives. These savvy assistants, powered by artificial intelligence, are like helpful neighbors who understand our needs and respond accordingly. Think of Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant – they’re not just software but more like digital buddies. They remind us of important appointments, answer our curious questions, keep our schedules on track, and even manage our smart homes. What’s great is that they learn about us as we interact with them, making their assistance more tailored and valuable as time goes by.
Top 5 AI Agents to consider:
#1 Navan AI
Navan.ai is the #1 rated multi-modal AI agent for fashion and e-commerce. It is the world's first AI agent specifically designed to help fashion and e-commerce businesses leverage artificial intelligence. Navan.ai enables businesses to create computer vision AI agents without the need for coding, allowing them to train AI to analyze images and videos, thereby unlocking valuable potential for their operations.
IBM Watsonx Assistant is a powerful AI-driven conversational platform designed to streamline customer interactions. It enables businesses to build intelligent virtual assistants that can handle customer queries, provide personalized support, and automate tasks across various channels. With advanced natural language processing and machine learning capabilities, Watsonx Assistant enhances user experiences, improves operational efficiency, and adapts to evolving customer needs, all while being easy to integrate and customize.
#3 Spell
Spell offers a sleek user interface with a powerful AI agent powered by GPT-4 underneath. It automates daily tasks and, with web access enabled, enhances productivity even further. Unlike OpenAI ChatGPT, which handles a single prompt at a time, Spell allows multiple prompts to run simultaneously. Simply hit play, input your ideas, topics, or data, and watch as the AI transforms your content. Plus, Spell provides an impressive array of curated templates and prompts to help you get started.
#4 Synthflow
Synthflow is an AI voice agent for handling inbound and outbound calls, perfect for scheduling appointments, qualifying leads, and sending reminders. No programming skills are needed to create a voice assistant that can manage calls and book appointments 24/7. Customize agents to fit your needs or use them as is. Instantly upload data from PDFs, CSVs, PPTs, URLs, and more, making your agent smarter with each new data point.
#5 Fini
Fini can transform your knowledge base into an AI-driven chat in just 2 minutes—no coding required. This 24/7 AI agent seamlessly integrates with platforms like Discord and Slack, enhancing your interactive chat capabilities. Boost user engagement and retention by ensuring customers receive immediate answers anytime. If the AI encounters an issue, customers are smoothly transitioned to a human representative, ensuring continuous support.
Conclusion
AI agents represent a significant leap in technological evolution, blending artificial intelligence with human-like interaction and decision-making. As partners in strategic decision-making and customer engagement, their influence is set to grow. With AI Agents, businesses can harness these intelligent agents to drive innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. AI agents accelerate processes and support everyday work, offering students opportunities to specialize in AI and work on innovative projects, while lecturers can optimize teaching and create more effective educational experiences.